Pharmacokinetics – ADME
Excretion
What are the factors affecting excretion of a drug?
Various routes by which drugs can be eliminated
- Most important
- kidney
- liver
- Less important
- bile
- sweat
Main site of drug excretion = KIDNEYS
Impaired renal function = impaired drug excretion (if drug is mainly renally excreted)
Drugs also excreted in bile, sweat, lungs, breast milk, tears, genital secretions, saliva
Factors affecting drug excretion
- Glomerular filtration
- Normal GFR is about 120ml/min
- Rate of urine production is about 1-2mL/min.
- Drugs can be filtered at the glomerulus
Renal failure
- Creatinine is a substance produced in skeletal muscle which is excreted through the kidneys
- It is neither passively reabsorbed nor actively secreted
- Estimation of creatinine clearance, estimates clearance of drugs filtered at glomerulus
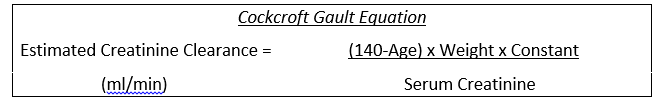
- Age in years
- Weight in kilograms
- Serum creatinine in micromol/litre
- Constant 1.23 for men 1.04 for women
Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate – GFR
- Renal function in adults is increasingly being reported as eGFR
- eGFR uses serum creatinine, age, sex and race (for African-Caribbean patients).
- This is normalised to a body surface area of 1.73m2 and derived from a specific formula.
- Absolute GFR = eGFR x individual’s body surface area /1.73
Which patients will have altered renal function?
- Elderly
- Reduced renal mass
- Reduced renal blood flow
- Neonates
- Patients with renal impairment
- Acute
- Chronic
| Grade | GFR | Serum Creatinine |
|---|---|---|
| Mild | 20-50ml/min | 150-300 micromol/L |
| Moderate | 10-20ml/min | 300-700 micromol/L |
| Severe | < 10ml/min | > 700 micro mol/L |
| Degree of impairment | eGFR mL/minute/1.73 m2 |
|---|---|
| Normal - Stage 1 | More than 90 (with other evidence of kidney damage) |
| Mild - Stage 2 | 60–89 (with other evidence of kidney damage) |
| Moderate - Stage 3 | 30–59 |
| Severe - Stage 4 | 15–29 |
| Established renal failure - Stage 5 | Less than 15 |
Rule of thumb: Assume every elderly patient has at least mild renal impairment
Copyright eBook 2019, University of Leeds, Leeds Institute of Medical Education.