This is the algorithm for advanced paediatric life support. Following initial CPR (5 rescue breaths then 15 chest compression to 2 breaths), the rhythm on the defibrillator will then determine further management.
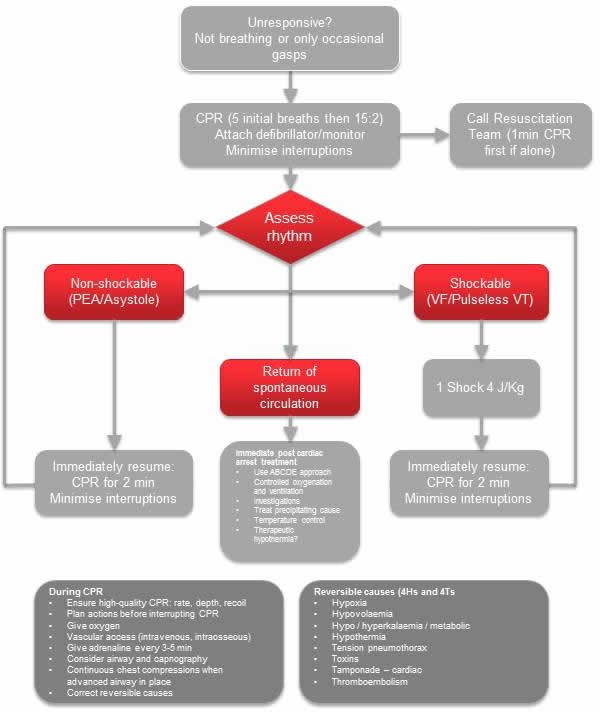
If the rhythm is PEA or asystole (non-shockable rhythms), then CPR must continue as above with the use of IV adrenaline every 3 – 5 minutes.
If the rhythm is Ventricular fibrillation (VF) or pulseless Ventricular Tachycardia (shockable rhythms which are much less common in children) then unsynchronised DC shocks are required. Adrenaline IV (10 micrograms/kg) is given after the 3rd shock and then every alternate shock, with amiodarone (5mg/kg) given only after the 3rd and 5th shock.
It is important to simultaneously think through the reversible causes of cardiac arrest and treat them as you go along. These are thought of as being the 4 H’s and 4 T’s. (Hypoxia, Hypovolaemia, Hypo/hyperkalaemia, Hypothermia, Toxins, Tension pneumothorax, Tamponade (cardiac), Thromboembolism).